Choosing between SketchUp vs AutoCAD depends on the project type, level of precision required, and user experience level. Both are powerful tools, but they cater to different types of users and project needs. Here’s a comparative breakdown to help you determine which one might suit you better:
1. Purpose and Use Cases
- SketchUp: Known for its user-friendly interface and ease of use, SketchUp is ideal for creating quick, visually detailed 3D models. It’s commonly used in:
- Architectural and interior design concept modeling
- 3D printing and fabrication
- Landscape architecture and simple urban planning
- Product and furniture design
- AutoCAD: A versatile CAD software, AutoCAD is a standard in the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries for 2D drafting and 3D modeling. It’s commonly used in:
- Precision 2D drafting, blueprints, and technical documentation
- Complex 3D modeling for engineering and manufacturing
- Civil engineering, mechanical, and electrical designs that require high precision
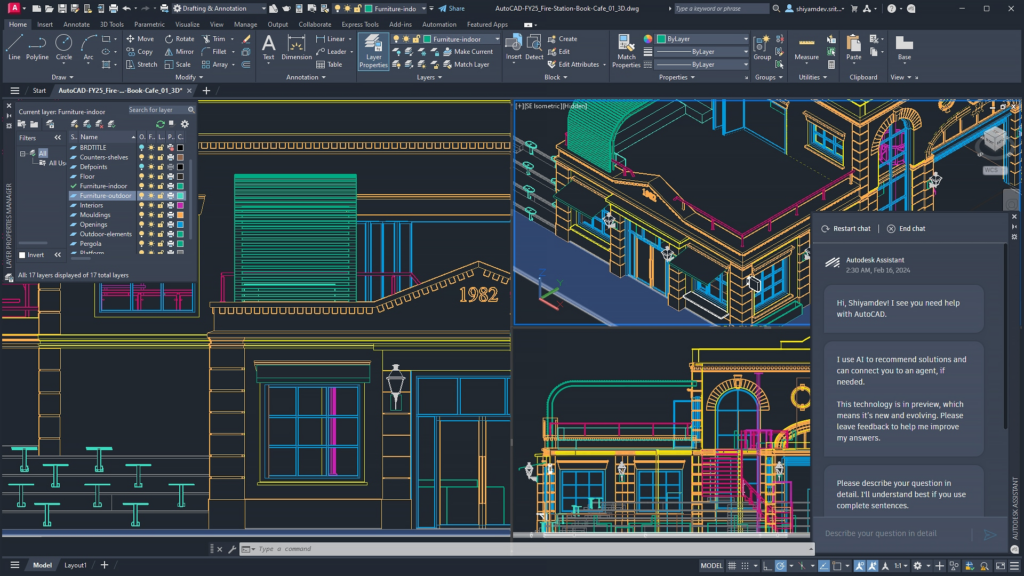
2. User Interface and Learning Curve
- SketchUp: Has a simpler, more intuitive interface with a shorter learning curve, especially for 3D modeling. It’s a favorite among beginners, hobbyists, and designers who need basic but quick modeling solutions.
- AutoCAD: While highly powerful, AutoCAD’s interface can seem complex to new users, especially with its array of commands and settings for 2D drafting and 3D modeling. It requires a longer learning curve, but experienced users appreciate the depth and control it provides.
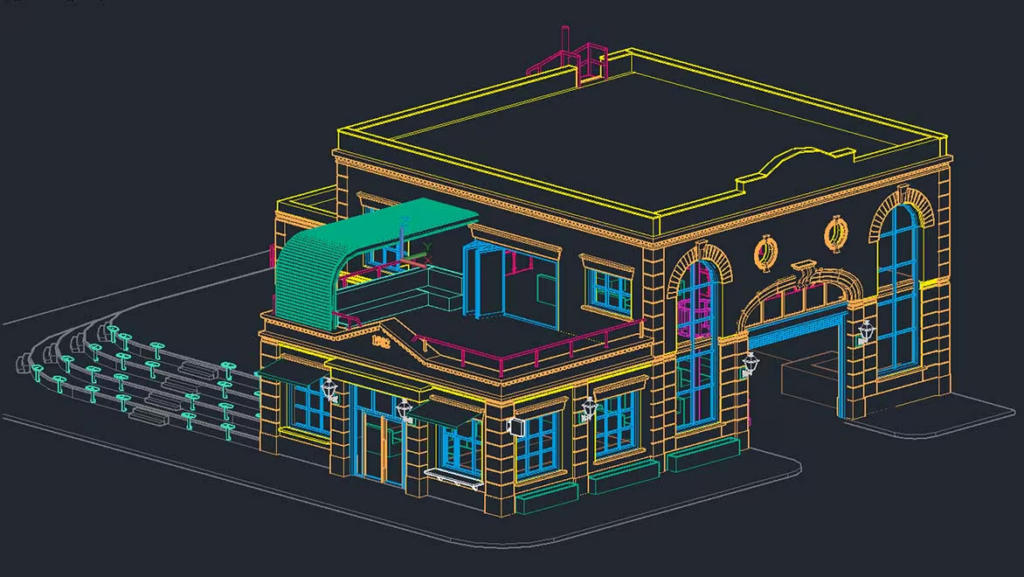
3. 3D Modeling Capabilities
- SketchUp: Offers intuitive tools for 3D modeling with a focus on creativity and visual design rather than precision. It’s excellent for architectural visualization and rendering, and its models are easy to share and modify.
- AutoCAD: Known for precision in both 2D and 3D, AutoCAD is more suitable for intricate designs requiring exact measurements. AutoCAD 3D modeling is capable but typically more rigid and detailed compared to SketchUp.
4. 2D Drafting and Documentation
- SketchUp: Has limited 2D drafting capabilities, though it does include LayOut, a tool for creating presentations and simple documentation from 3D models.
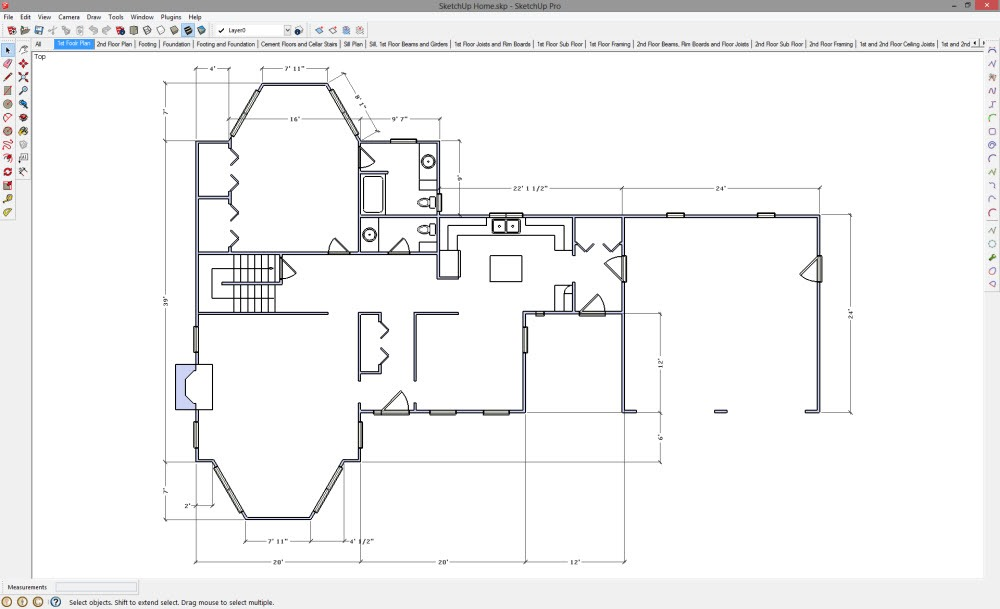
- AutoCAD: Exceptional at 2D drafting and technical documentation, making it the go-to software for architects and engineers who need high-quality, precise plans and blueprints.
5. Integration and Compatibility
- SketchUp: Exports to common file types like .DWG, .DXF, and .OBJ but doesn’t support as many file formats as AutoCAD. It integrates well with design visualization software like V-Ray for rendering.

- AutoCAD: Provides extensive compatibility with a range of file formats and supports integration with industry-standard software, such as Revit, Civil 3D, and other Autodesk products, which is valuable for professionals who work in a collaborative, multi-software environment.
6. Pricing
Here’s a comparison of the pricing for SketchUp and AutoCAD in the United States:
| Software | Plan | Price (Annual) | Price (Monthly) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SketchUp | SketchUp Free | Free | N/A | Basic features for personal use. |
| SketchUp Go | $119 | N/A | Web-based modeling with mobile app access. | |
| SketchUp Pro | $299 | N/A | Desktop modeling with advanced features. | |
| SketchUp Studio | $1,199 | N/A | Includes additional tools like Sefaira for energy analysis. | |
| AutoCAD | AutoCAD LT | $515 | N/A | 2D drafting and documentation. |
| AutoCAD | $2,030 | N/A | Comprehensive 2D and 3D design tools. |
- SketchUp: Offers a free web version with basic 3D modeling capabilities, while its Pro and Studio versions require an annual subscription. SketchUp Pro is typically less expensive than AutoCAD.
- AutoCAD: Available only through a paid subscription, with a higher cost, reflecting its professional-grade tools and capabilities.
7. Community and Support
- SketchUp: Known for an active community with an extensive 3D Warehouse library for free model sharing and collaboration.
- AutoCAD: Supported by Autodesk’s extensive resources and has a broad professional community with deep expertise and training resources.
SketchUp VS CAD ?
Here’s a table comparing SketchUp with CAD software:
| Feature | SketchUp | CAD (AutoCAD, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | 3D modeling, architectural design | 2D drafting, technical drawings, 3D modeling |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, intuitive UI | Steeper learning curve, more technical |
| Precision | Good for conceptual design, less precise | High precision for engineering & manufacturing |
| File Formats | Supports SKP, DWG, DXF, STL, OBJ, etc. | Supports DWG, DXF, PDF, STL, etc. |
| 2D Drafting | Limited 2D drafting tools | Extensive 2D drafting tools |
| 3D Modeling | Fast and intuitive 3D modeling | More complex, parametric capabilities |
| Rendering | Plugins required (V-Ray, Enscape, etc.) | Some CAD software have built-in rendering |
| Collaboration | Cloud-based collaboration (Trimble Connect) | File-based collaboration, BIM integration |
| Industry Use | Architecture, interior design, woodworking | Engineering, manufacturing, construction |
| Cost | Free version available, Pro version paid | Typically more expensive |
- Choose SketchUp if you need a more user-friendly, flexible tool for 3D modeling, especially for visual projects like architecture, interior design, or creative concepts that don’t require ultra-precise measurements.
- Choose AutoCAD if you’re working on technical, detailed designs that require high precision in 2D or 3D, or if you’re involved in engineering, construction, or manufacturing projects.
In essence, SketchUp is best for quick 3D conceptualization, while AutoCAD is ideal for precise drafting and detailed documentation.



