Finding the volume of an object in SketchUp can be done using its built-in tools, provided the object is a solid group or solid component. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Ensure the Object is a Solid
- For SketchUp to calculate volume, the object must be a solid. This means:
- The object must be a group or a component.
- The geometry must be completely enclosed (no holes or gaps).
- No stray edges, open faces, or internal geometry.
Check if the Object is a Solid:
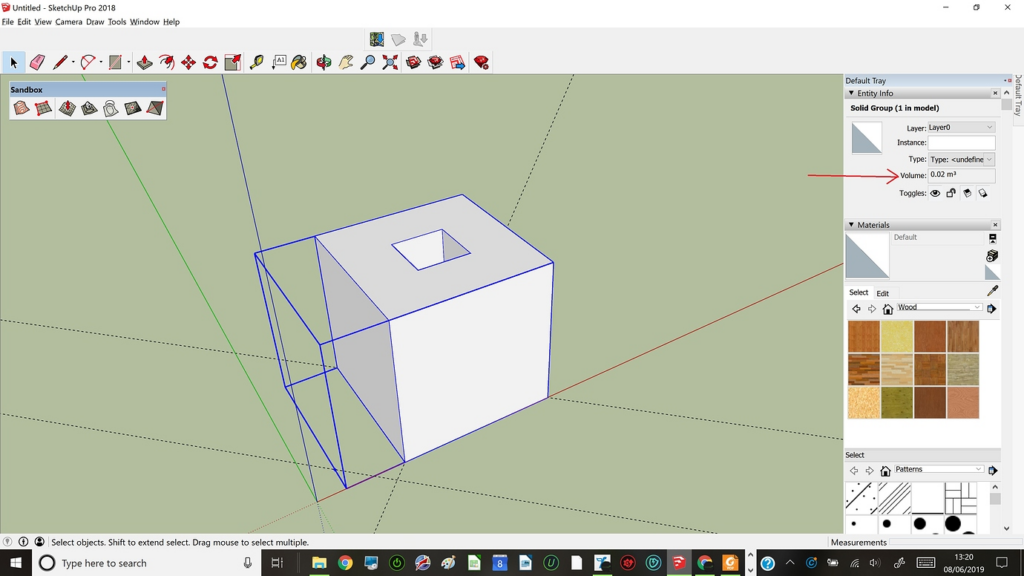
- Select the object.
- Look at the Entity Info panel (Window > Entity Info).
- If it says “Solid Group” or “Solid Component,” the object is a valid solid.
- If not, you’ll need to fix the geometry before SketchUp can calculate the volume.
2. Find the Volume
- Select the Solid Object:
- Use the Select Tool (spacebar) and click the object.
- Open Entity Info:
- Go to Window > Entity Info.
- The volume will be displayed in the Entity Info panel, typically in the default units of the model (e.g., cubic feet, cubic meters, etc.).
3. Fixing Issues with Non-Solid Objects
If the object isn’t recognized as a solid, follow these steps:
- Inspect for Gaps:
- Use the Tape Measure Tool or Zoom Extents to locate small gaps or holes.
- Close any openings using the Line Tool (
L) or the Eraser Tool (E).
- Remove Stray Geometry:
- Delete extra edges, floating lines, or faces that don’t contribute to the enclosure.
- Use Extensions:
- Install extensions like Solid Inspector2 (available from the Extension Warehouse) to identify and fix issues preventing the object from being a solid.
4. Alternative Method: Manual Volume Calculation
If the object cannot be converted to a solid:
- Divide the object into measurable parts (e.g., cubes, cylinders, or spheres).
- Calculate the volume of each part manually using standard formulas:
- Cube: V=length×width×heightV = \text{length} \times \text{width} \times \text{height}V=length×width×height
- Cylinder: V=π×radius2×heightV = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \times \text{height}V=π×radius2×height
- Sphere: V=43π×radius3V = \frac{4}{3} \pi \times \text{radius}^3V=34π×radius3
- Sum the volumes of all parts.
5. Use Extensions for Complex Shapes
For complex objects, consider using extensions like:
- Volume Calculator: Offers enhanced volume measurements for irregular shapes.
- Eneroth Solid Tools: Provides additional tools to combine, subtract, and analyze volumes.
Summary
- Ensure the object is a solid.
- Check the Entity Info panel for the volume.
- Fix non-solid geometry if necessary using tools or extensions.
- Use manual or plugin-based methods for non-solid or irregular objects.



